In the heart of many homes and industrial facilities, the unassuming yet vital appliance known as the boiler quietly works its magic. Providing warmth and comfort during cold winter months, powering industrial processes, and ensuring the availability of hot water, boilers play a crucial role in our daily lives. This article delves into the world of boilers, exploring their types, functioning, applications, and environmental considerations.
A Brief Introduction to Boilers
A boiler is a closed vessel designed to heat water or other fluids to generate steam, which is then used for various purposes. The concept of heating water to produce steam has been a cornerstone of human progress for centuries. The earliest instances of steam utilization can be traced back to ancient civilizations like the Greeks and Egyptians. However, the industrial revolution marked a turning point in the development of boilers, as they became integral to powering machines and facilitating various industrial processes.
Types of Boilers
Boilers come in various types, each designed to cater to specific needs and applications. Some common types include:
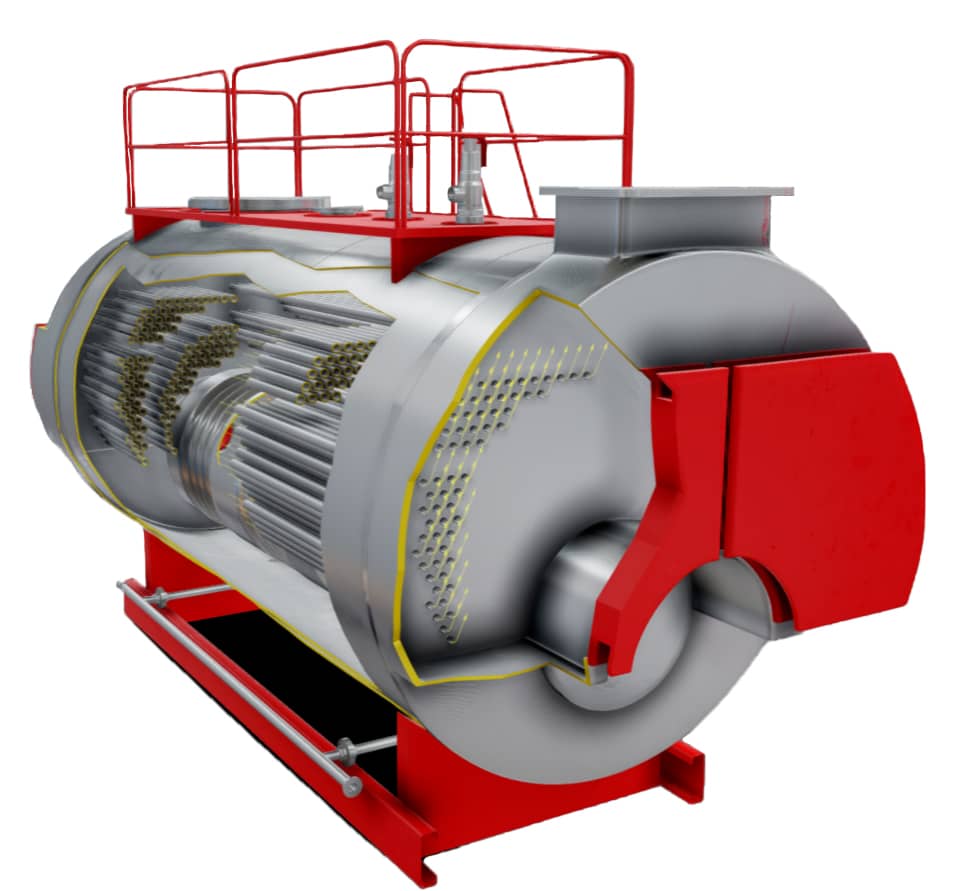
Fire-Tube Boilers: These are one of the oldest types of boilers, characterized by a cylindrical shell containing water, with fire tubes running through it. The heat from the combustion of fuel is transferred to the water through the tubes, generating steam.
Water-Tube Boilers: In this type, water circulates through tubes that are heated externally by hot gases. Water-tube boilers are known for their efficiency and ability to handle higher pressures, making them suitable for industrial applications.
Steam Boilers: Steam boilers are designed to produce steam for various purposes, including heating, power generation, and industrial processes. They are commonly used in power plants and manufacturing facilities.
Hot Water Boilers: Hot water boilers are designed to provide hot water for heating purposes in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. They are often used for radiant floor heating, space heating, and domestic hot water supply.
Condensing Boilers: These boilers are designed to capture and utilize the heat that would normally be lost in the exhaust gases. They are highly efficient and environmentally friendly, making them a popular choice for modern heating systems.
How Boilers Work
The basic principle behind boiler operation is to transfer heat from a fuel source to water, generating steam or hot water in the process. Here’s a simplified breakdown of how boilers work:
Fuel Combustion: Boilers can be fueled by a variety of sources, including natural gas, oil, coal, biomass, and even electricity. The chosen fuel is burned in a combustion chamber, producing heat.
Heat Transfer: The heat generated by the fuel combustion is transferred to the water or fluid within the boiler. In fire-tube boilers, this heat transfer occurs through the walls of the tubes, while in water-tube boilers, the hot gases flow over the exterior of the tubes.
Steam Generation: As the water absorbs the heat, it begins to boil and transform into steam. The steam can then be used for various applications, such as powering turbines for electricity generation, heating spaces, or driving industrial processes.
Control and Safety: Boilers are equipped with various controls and safety mechanisms to ensure safe and efficient operation. These include pressure relief valves, temperature sensors, and automatic shut-off systems.
Applications of Boilers
Boilers find extensive use across a wide range of industries and settings:
Residential Heating: In homes, boilers are used to provide central heating and hot water for domestic use. Radiators, underfloor heating systems, and baseboard heaters are commonly used to distribute the heat produced by boilers.
Industrial Processes: Many industrial processes, such as chemical production, food processing, and paper manufacturing, rely on steam generated by boilers. Steam is often used for heating, sterilization, and mechanical power.
Power Generation: Power plants use boilers to generate steam, which drives turbines to produce electricity. Different types of power plants, such as coal-fired, natural gas-fired, and nuclear plants, rely on boilers for steam generation.
Commercial Buildings: Boilers are used in commercial buildings for space heating and hot water supply. Hotels, hospitals, schools, and office buildings often rely on boilers to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures.
Environmental Considerations
While boilers play a crucial role in various industries, their environmental impact cannot be overlooked. The combustion of fossil fuels in boilers releases greenhouse gases and other pollutants into the atmosphere, contributing to climate change and air pollution. To address these concerns, there has been a growing emphasis on adopting cleaner and more sustainable technologies:
High-Efficiency Boilers: Modern boilers are designed to be more efficient, reducing fuel consumption and emissions. Condensing boilers, for example, capture and reuse heat that would otherwise be wasted.
Renewable Energy Integration: Biomass boilers, which use organic materials as fuel, and solar thermal systems can help reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Integrating renewable energy sources into boiler systems can lower carbon emissions.
Emission Control Technologies: Advanced emission control technologies, such as selective catalytic reduction (SCR) and electrostatic precipitators, help reduce pollutants from boiler exhaust gases.
Conclusion
Boilers have come a long way from their humble beginnings as vessels that heated water to produce steam. Today, they are essential components of modern living, powering industries, heating homes, and driving technological progress. As we continue to prioritize sustainability and environmental responsibility, the evolution of boiler technology will play a pivotal role in shaping a cleaner and more energy-efficient future. Whether it’s through higher efficiency, renewable integration, or emission control, the boiler’s journey is one of adaptation and innovation to meet the ever-changing needs of society.