What is API?
API is an acronym for Application Programming Interface, which is a set of programming codes that enables data transmission, queries data, parses responses, and sends instructions between one software platforms to another. Enterprise developers greatly rely on Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) for the development and delivery of applications and services.
API can also hide complexity from developers, allowing them not to waste time on how a service works from scratch. API can also be used to extend functionality of a systems and can also act as a gatekeeper to safeguard user’s data.
API have become an increasingly popular tool. Big Organizations like Facebook, Google, Amazon and many more are launching their own APIs which permit other Organizations to access some of their services without having to fully migrate into their ecosystem. In simple term, API can also be simply defined as an intermediary software that enables two or more applications to communicate to one another without user intervention.
API Security

In recent years, API vulnerabilities has been exploited massively which leads businesses to millions of losses in revenue. API security is the protection of the integrity of APIs and the application of common security best practices implement to APIs, which are established in modern applications. API security includes API access control and privacy, as well as the detection and remediation of attacks on APIs and the exploitation of API vulnerabilities.
Since the main purpose of API is to transfer data and connect services, it is very vital for developers to be aware of how data are handled in the application’s APIs and to apply necessary security measures for it. API are often publicly available over open networks, so APIs are usually well documented or easily reverse-engineered by attackers. Hence the requirement for drastic security measure.
SOAP, REST and GraphQL Security
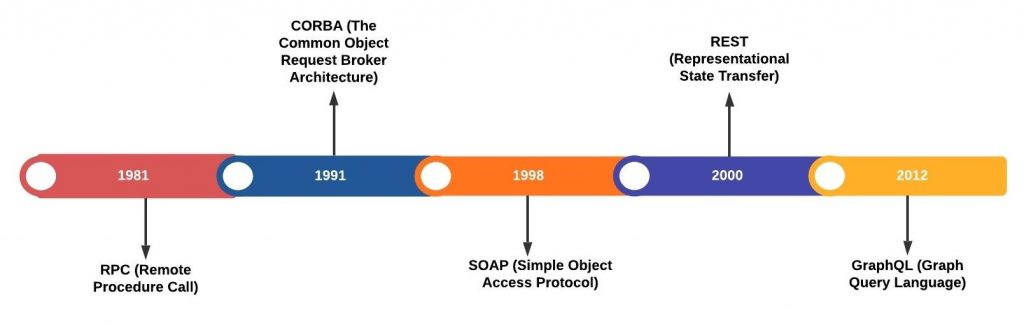
SOAP (Simple Objects Access Protocol) is a web communication protocol designed mostly used to expose web services and transmit data over HTTP/HTTPS. It supports the XML data format only and strongly follows standards such as messaging structure, a set of encoding rules, and a convention for providing procedure requests and responses. The SOAP style of security is applied at the message level using digital signatures and encrypted parts within the XML message itself.
REST (Representational State Transfer) uses HTTP to obtain data and perform operations on remote computer systems. It is an architectural style, rather than a protocol and supports SSL authentication and HTTPS to achieve secure communication. REST can operate with JSON, XML, HTML, and other formats for consuming API payloads, which simplifies data transfer over browsers. HTTPS coverage acts as a shield for data security. And SSL security protocol is applied over an HTTPS connection to verify REST APIs calls REST is the most common type of API security used over the past decade.
GraphQL, an emerging open-source query language API project. GraphQL gives huge power to clients. Since clients have the possibility to craft very complex queries, our servers must be ready to handle them properly.
API Common Vulnerabilities and Threats
API give access to clients and at the same time also lures potential attackers to the backend systems. The potential attack surface of any application is increased by using API as the security environment is moved from secure backend system to user’s devices.
According to Gartner,” exploiting APIs will be the most common attack vector for data breaches within enterprise web applications by 2022.” Data breaches are continuously happening through APIs vulnerabilities because sensitive data are constantly flowing through APIs. API security also include looking at the structured data coming into and going out through your APIs and enforcing rules at the data layer.
OWASP API Security Top 10
It is essential for an organization to understand different types of threats in order to defend against it. Some of the commonly known Vulnerabilities are listed in OWASP TOP 10 API VULNERABILITIES which are as below:
- Broken Object Level Authorization
- Broken User Authentication
- Excessive Data Exposure
- Lack of Resources & Rate Limiting
- Broken Function Level Authorization
- Mass Assignment
- Security Misconfiguration
- Injection
- Improper Assets Management
- Insufficient Logging & Monitoring
The list itself covers a wide scope of API Security threats. Therefore, the need for security and protection mechanism against the new classes of threats increases as a result of implementing APIs.
API Penetration testing
A Penetration Testing is a simulated cyber-attack against a system to analyze it for vulnerabilities. During API Penetration testing, API functions and methods are examined and attempt to be compromised and see how it can be abused. API are also tested for different common vulnerabilities like Cross Site Scripting, Command Code Injection, Access control, encryption, authentication etc.
It is vital for Businesses to continuously test API security and look at it through an API lens. API security testing should be incorporated into the ongoing quality testing of APIs. In some cases, calling an API in ways an application does not normally do leads to sensitive data exposure.
API Pentesting Methodology
There are several lists of industry standards for API Pentesting Methodology. Some of the main ones use widely today are:
- Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) Testing Guide
- OWASP API Security Top 10 (2019)
- Technical Guide to Information Security Testing and Assessment (NIST 800-115)
- The Penetration Testing Execution Standard (PTES)
- Payment Card Industry (PCI) Penetration Testing Guidance
The API Penetration Testing can be broken down into the following stages.
RECONAISSANCE
During this phase, various sources will be inspecting to gather as much information about the target as possible, including researching the organization, generating threat intelligence, and enumerating attractive services within the network
THREAT MODELLING
During the threat modeling, the threat modeling phase serves to evaluate the types of threats that may affect the target APIs that are in scope. Any information gathered during the Reconnaissance phase is used to inform the method of attack during the penetration test.
EXPLOITATION
With a map of all potential API vulnerabilities endpoints, testing on Application, network and data is done at this stage as an attacker would. The goal here is to analyze the impact of the API vulnerability in the Organization’s system. Manual identification and confirmation of vulnerabilities for each tested endpoint can also be performed, including server and client-side vulnerabilities, injection-attacks, error analysis, file uploads, etc.
POST EXPLOITATION
Post exploitation processes involve risk analysis and recommendations. It aims to record the techniques exploited to gain access to an organization’s critical assets. The tester determines the significance of the compromised system and the significance of the collected data.
REPORTING
The Pentester gathers all the steps and details of the exploitation and document the techniques exploited to access to an organization’s critical asset. The Pentester makes a detailed report covering all the activities and technique involved to penetrate the Organization Asset.Implementation of APIs have led to a massive digital transformation within the cloud, IoT, mobile and web applications.
Identifying attacks on APIs is not an easy task, it requires a skilled professional to detect and remediate API vulnerabilities. Attacks against API are continuously increasing overtime and become one of the most attack types. Walnut Security Services will help analyzes your API and depending on your requirement provide protection to your organization’s assets from any potential threats,