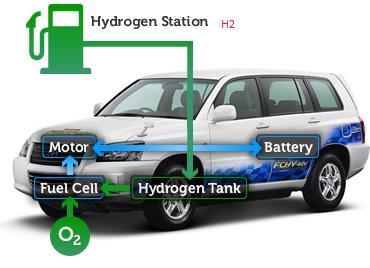
A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell in which a direct DC current is generated by the reaction of hydrogen and oxygen. Currently, hydrogen-fueled buses and cars can be seen in countries like Japan, South Korea, America, and Germany. So much for foreign affairsFuel cell cars are powered by highly compressed hydrogen gas that feeds into an onboard fuel cell “stack” that does not burn the gas, but instead converts the chemical energy of the fuel into electrical energy. This electrical energy then powers the vehicle’s electric motor.
In the current modern era, the automobile sector has been most influenced by fuel cell technology. Fuel cell vehicles have expressed a general research interest among big names in the automobile industry. The electricity obtained by the fuel cell is used to power a motor which acts as torque to provide rpm to the transmission system.
Electrical energy carries 85% of the efficiency of the mechanical power by the motor, leading to an overall efficiency (85% of the fuel cell + 85% of the motor) of about 70% (although there are some transmission losses), which is a huge increase compared to the 35% efficiency of a petrol engine. These numbers apply to a fuel cell using pure hydrogen.
As of 2015, there are two models that are commercially available and tested, the Hyundai IX35 FCEV and the Toyota Mirai, although they were released in limited quantities. There are many more concept cars released by automobile companies like Honda (FCX Clarity and FCV Concept), Audi (A7 h-Tron Quattro), Mercedes Benz (F-Cell and F800), and Volkswagen (Golf Hymotion) and Nissan (TeRRA FCV SUV). A ) The most efficient models involve the use of pure hydrogen which can increase the weight and therefore sometimes hydrogen compounds are used which are worked by adding an additional device called a “reformer” to extract the hydrogen.
Now we may still have doubt about why battery-powered cars are not good enough to work. Although batteries have more capacity than fuel cells (about 90%), they cannot produce any energy of their own. The electricity used to recharge the batteries has to come from somewhere, and that energy is environmentally friendly or may not be generated in an efficient manner.
Why Fuel Cells?
The main reason why fuel cells hold promise in power generation is that they act as environmentally friendly. Fuel cells use water as their main byproduct which is another big advantage. Since conversion to low-grade energy such as thermal energy is now being eliminated, they are highly efficient, converting 85% or even 95% ie 85% of the energy released from chemical reactions into electricity.
Dependence on fossil fuels must be ended so that life on Earth can comfortably survive and not destroy the environment, and this is why scientists and engineers are constantly working toward finding better ways to produce energy. Fuel cell technology may be the answer but currently, this technology is not strong enough to replace conventional power generation. They have issues with cost, durability, storage, malfunctioning, and other considerations. Countries are also working to produce hydrogen in environmentally friendly ways and have formed an “International Partnership for the Hydrogen Economy” among 18 countries. Hydrogen is the most abundant energy element present in the universe and powers stars. When we use this gift of nature, we must obey the laws of nature.
Conclusion:
So now some automakers believe hydrogen fuel-cell vehicles can secure a place in the automobile’s new, more fragmented future. So could synthetic biofuels, hybrids, autogas carbon, and other powertrains, as engineers move in new directions exploring multiple technologies to balance decarbonization with consumer needs.