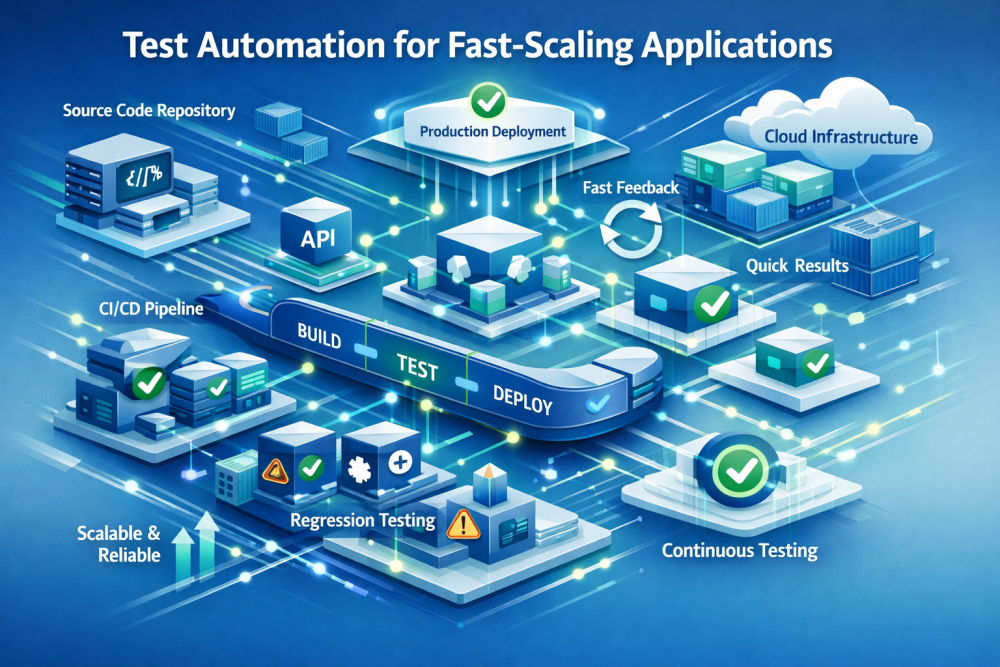
Introduction
As a software product grows, things tend to move faster than expected. Teams push out features more often, different parts of the system start depending on each other, and changes reach production with very little gap in between. Over time, this makes it easier for small mistakes to go unnoticed and cause issues later on.
Because of this, relying only on manual testing becomes harder as the application scales. Testing needs to keep up with frequent changes, and consistency becomes critical. Test automation helps teams manage this pressure by making testing repeatable and reliable as systems continue to evolve.
The Reality of Scaling Applications
The reality about scaling applications is that they operate in a constantly changing world. The codebase will grow over time, and new APIs will continue to expand in functionality while multiple teams build their own features (code) simultaneously. Releases may occur every week or in some cases, even daily.
Here are some characteristics of scaling systems:
- Single code changes occur often across multiple services.
- Rapid API Changes and integration occur frequently.
- Short cycle times between releases are mostly in CI / CD prepared pipelines.
- Higher expectations from users around an application being available without fault.
Lack of a solid testing strategy could potentially lead to issues resulting from small code changes. After time passes, those types of code changes will create additional delays, which ultimately increase production risk.
Why Manual Testing Stops Working at Scale?
The limitations of manual testing become apparent during the later phases of development when the application is more complex than the testing process itself.
Limited coverage
As applications become larger, it becomes impractical to validate all scenarios, integrations, or edge cases through manual testing.
Longer release cycles
As the number of tests increases with each release, the amount of time required for manual regression testing also increases, which in turn delays the ability to deploy or speed up delivery.
Inconsistent results
When different testers perform the same tests in different ways, the results are not repeatable and cannot be relied on to accurately represent the application.
Significant maintenance burden
When test cases are updated due to feature changes or additions, the test case needs to be revised; maintaining large numbers of manual test cases is expensive and inefficient.
These limitations have made the continued use of manual testing methods for rapidly scaling applications unsustainable in the long run.
How Test Automation Supports Growth?
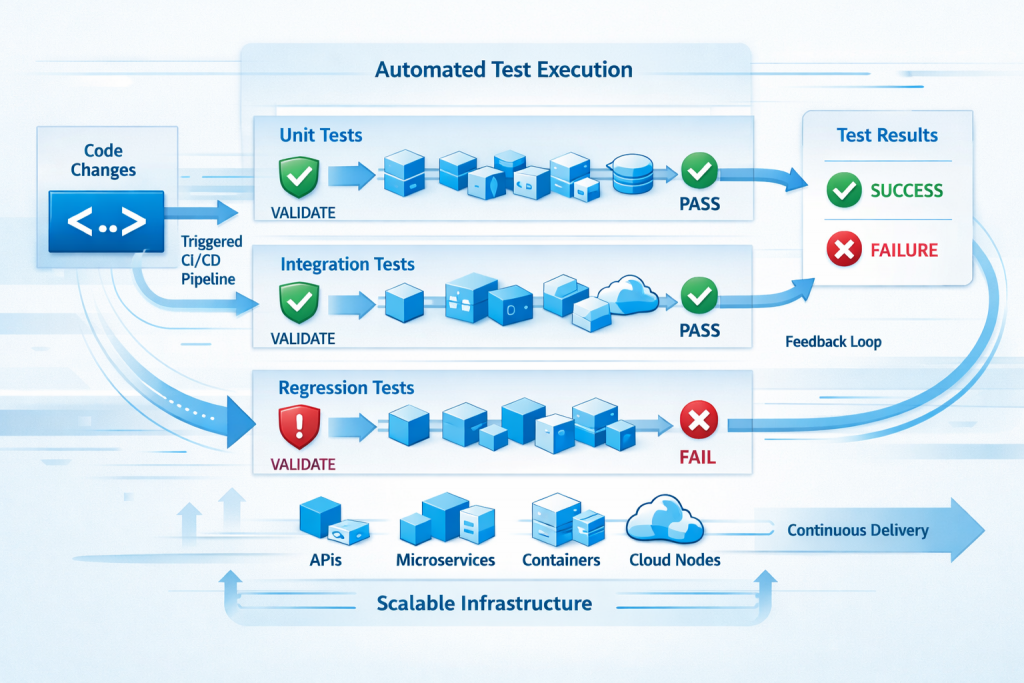
Test automation allows teams to scale without compromising with the quality. When implemented correctly, it becomes part of the development workflow rather than a separate phase.
- When code is modified, you will get fast feedback with automated tests since they run automatically after you modify the code.
- Automated Tests can also identify any regressions in your code early and enable you to implement a CI/CD pipeline.
- When an automated test runs after a modification has been made, the developers know that their existing functionality has not changed while adding new features.
Ultimately, over time, the use of test automation reduces the amount of time spent performing repetitive tasks. As a result, development teams will be able to dedicate their time to developing and enhancing their products rather than retesting the same functionality.
The API Testing Challenge in Growing Systems
APIs Have a Central Role as the Systems Grow. Modern Applications Often Use Internal Systems, Third-Party Integrations, and Distributed Architectures.
API testing becomes challenging due to:
- Frequent Changes in the Endpoints Used To Make Requests as Well as the Structure of the Requests.
- The Amount of Time Required to Create and Maintain the Test Cases.
- The Failure of the Tests Due to Changes In the Environment or Data.
- Limited Visibility Into the Actual Usage Patterns.
Traditional api testing methods have not kept pace with these changes, especially when tests are written and maintained manually.
Modern Approaches to API Test Automation
Teams are now moving towards more adaptive ways of creating automated API tests in order to eliminate manual effort while keeping the text consistent with actual application behaviour.
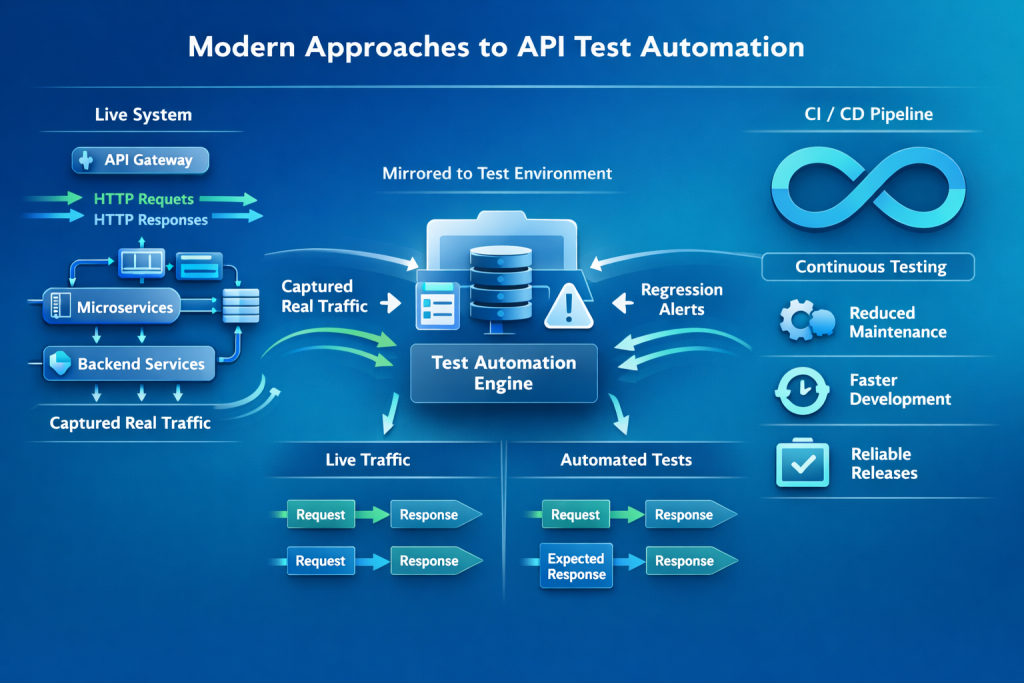
Some teams are using API Automated Testing tools that capture real request and response flows and use those captured flows in automated testing, i.e., they are using a traffic-based tool like Keploy to support an automated test for real APIs. This assists in reducing the maintenance of automated tests and also contributes to confidence in how an API will work through subsequent continuous releases.
The overall trend is moving towards developing automation solutions that increase development speed, rather than slowing it down.
Best Practices for Sustainable Test Automation
The goal of developing a sustainable test automation approach is to provide long-term reliability instead of just short-term testing coverage. Test automation solutions must be easy for testers to maintain over time, as applications must be enhanced or expanded.
Here are some key points to achieve a sustainable test automation strategy:
1. Focus on the Critical Nature of Workflows: Automated testing should focus on core user journeys, high-risk functionalities, and frequently used APIs as opposed to achieving full test coverage.
2. Develop Automation Early: Developing automation early in the development cycle will prevent the quality of tests from being compromised due to the expansion of your codebase.
3. Create Maintainable Test Suites: Tests should be written so they can be easily understood and have modular functionality that can be updated when the functionality of the code is changed.
4. Integrate Automation into CI/CD Pipeline: Automated tests should run automatically with every build or deployment, resulting in the most rapid and valuable feedback.
5. Continuously Monitor & Refine: Keep track of execution times, trends, failures, and flaky tests, to provide a higher level of their reliability as time goes on.
If applied consistently, these best practices help teams build automation that scales with the application rather than becoming a maintenance burden. To sum up, the goal of test automation is not maximum automation, but reliable automation that provides steady growth and long-term stability.
Test Automation as a Long-Term Advantage
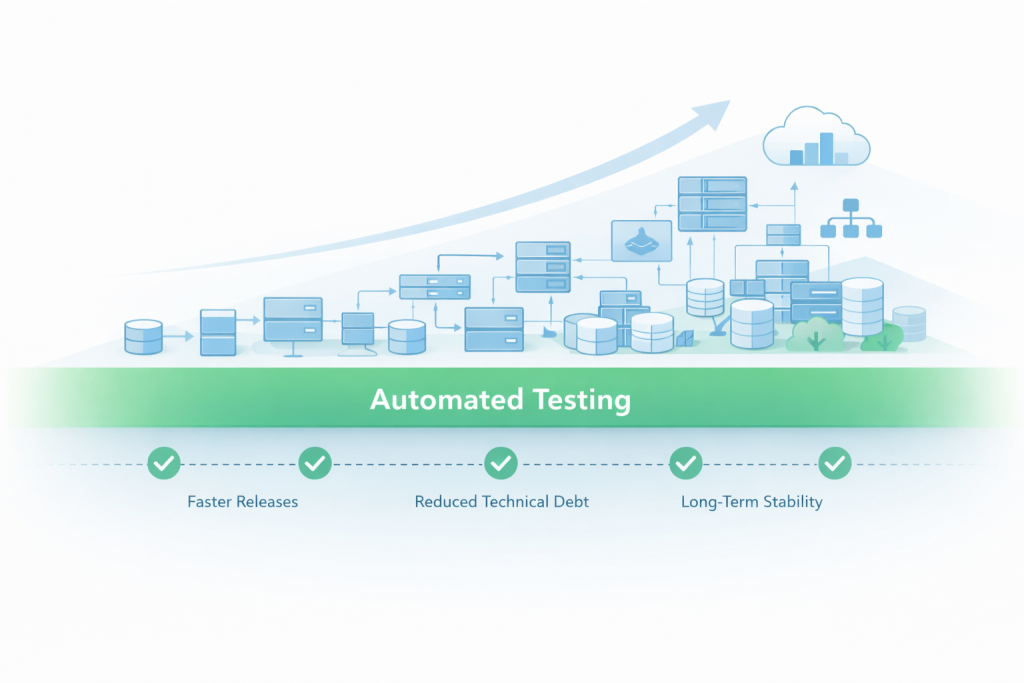
For fast-growing applications, test automation is a way of improving it technically, but It changes how quickly you can release, how stable your products are, and how effectively developers can create a product.
Teams that automate early have more capability to handle growing complexities than other teams do. In Addition to releasing faster, having fewer regressions, and being more confident when making production changes. Teams that wait to automate will eventually become more unstable due to the technical debt.
Conclusion
The increase in the size of a software application usually means the complexity will also increase. However, that does not mean that the quality must suffer. Using test automation as a way to create an automated test suite to give you the structure and reliability needed to help facilitate rapid growth.
By incorporating practical automation techniques and current API testing methodologies, teams of developers and testers can work quickly without sacrificing system stability. For fast scaling applications, using a method of automation testing is no longer an option. It has become a must.