In any organization, sales activities directly affect revenue, and financial records, SAP Sales and Distribution, commonly known as SAP SD, manages this entire flow in a structured way. From the moment a customer places an order to the point where payment is recorded in finance, SAP SD ensures that every step is connected.
Students who begin learning through an SAP SD Course are introduced to this process early being great investment option. They learn that SAP SD is about how data moves across modules and how one transaction triggers another.
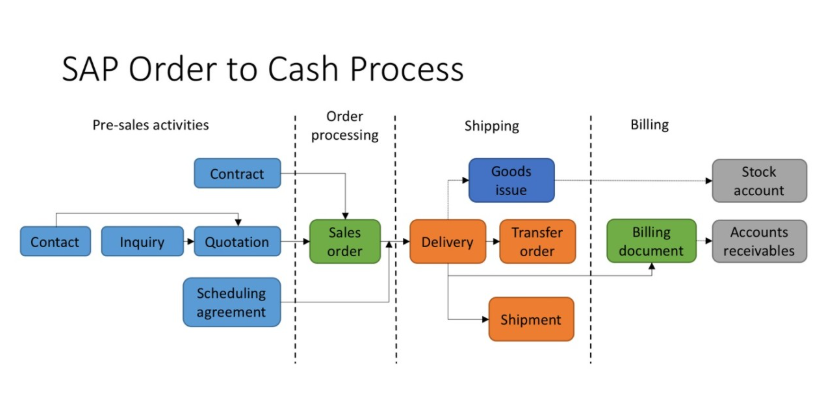
Overview of SAP SD Data Flow
The SAP SD data flow follows a clear sequence, it starts with customer demand and ends with financial posting. Each document created in the system carries information forward so that the next step does not need to start from scratch.
The main stages in SAP SD data flow include:
- Sales order creation.
- Delivery processing.
- Goods issue.
- Billing and invoicing.
- Financial posting in accounting.
Each stage updates data in real time, keeping sales, inventory, and finance aligned.
Sales Order Creation and Its Importance
The sales order is the foundation of the SAP SD process, it captures customer details with payment terms. Once created, this document becomes the reference point for all future transactions.
In practical sessions during an SAP SD course in Hyderabad, learners work with real examples. They understand how customer master data, and pricing conditions come together. Any mistake at this stage can affect delivery, and revenue reporting later.
Sales orders also perform availability checks with credit checks, this ensures that the company can deliver the product.
Delivery Processing and Logistics Integration
After a sales order is confirmed, the next step is delivery creation, the delivery document controls how goods are picked, and shipped. It connects SAP SD with warehouse and logistics functions.
Learners studying for an SAP SD Certification Course see how delivery documents reduce manual work. The system automatically copies relevant data from the sales order, such as shipping details. This avoids duplication and keeps information consistent.
Delivery processing also prepares the system for inventory updates, it ensures that stock movement is recorded correctly once goods leave the warehouse.
Goods Issue and Inventory Impact
Goods issue is the step where inventory is officially reduced. When goods issue is posted, SAP updates stock levels and records material movement.
During an SAP SD Course in Pune, learners observe how goods issue triggers multiple updates at once. Inventory decreases, accounting entries are prepared, and logistics status is updated. This step is critical because it confirms that goods have physically left the company.
Goods issue also plays a role in profitability analysis and cost tracking. It ensures that the cost of goods sold is calculated correctly.
Billing and Invoice Creation
Billing is the stage where revenue is officially recorded. The billing document is created based on the sales order or delivery, depending on the business process. It calculates the final amount the customer needs to pay, including taxes and discounts.
Students in SAP SD Training in Noida learn how billing types control invoice behavior. They work with standard invoices, credit memos, and debit memos. The system automatically pulls pricing details from the sales order, ensuring accuracy.
Billing documents are legally important, as they are often shared with customers and auditors. That is why SAP ensures strict control and traceability at this stage.
Financial Posting and Integration with Accounting
Once the billing document is posted, SAP automatically creates financial entries in the accounting module. This is where SAP SD integrates with finance.
Revenue, taxes, and customer receivables are updated in real time, there is no need for manual journal entries. This integration ensures that sales data is immediately reflected in financial reports, where learners understand that this automatic posting. It reduces errors, and keeps finance teams informed without delays.
Why Data Consistency Matters in SAP SD?
SAP SD data flow is designed to maintain consistency, and changes are tracked, this helps businesses audit transactions resolving issues.
For example, if a customer questions an invoice, the team can trace it back to the delivery. This transparency builds trust and improves internal control.
Training programs emphasize the importance of understanding these links instead of separating.
Common Challenges in SAP SD Data Flow
While SAP SD is powerful, problems can occur if configuration is incorrect, some common issues include:
- Incorrect pricing conditions.
- Missing master data.
- Delivery blocks not released.
- Posting errors during billing.
Learners are taught how to identify or fix these issues by understanding flow breaks.
Conclusion
SAP SD data flow connects sales activities with logistics in a structured way building on the previous one with accuracy. Understanding this flow is essential for anyone working with SAP systems with proper training through mentioned courses. This will make you confident in managing SAP SD Business Process with supportive business operations.