Understanding the difference between Angioplasty vs Stent is vital when it comes to handling heart- related extremities effectively. In moment’s presto- paced world, where cardiovascular conditions are among the leading causes of death encyclopedically, knowing how these two procedures differ and when each is used — can make all the difference in timely treatment. Especially in settings like Urgent Care, where rapid-fire decision- timber and original stabilization play critical places, distinguishing between angioplasty and stent placement becomes indeed more essential.
This composition explores the top seven crucial pieces of data about angioplasty and stents, shedding light on how they’re performed, their benefits, and their part in critical cardiac care.
1. Understanding the Basics: What’s Angioplasty?
Angioplasty is a minimally invasive procedure designed to open narrowed or blocked coronary highways. It’s frequently performed when blood inflow to the heart muscle becomes defined due to shrine buildup, a condition known as coronary roadway complaint( CAD). During angioplasty, a small balloon- sloped catheter is fitted into the blocked roadway and inflated to widen it, restoring normal blood inflow.
This procedure can relieve casket pain( angina), ameliorate heart function, and reduce the threat of heart attack. It’s frequently the first line of treatment during emergency heart procedures when time is of the substance.
2. What’s a Stent and How Does It Work?
A stent is a small, mesh-like tube placed inside the roadway after angioplasty to keep it open. While angioplasty widens the roadway temporarily, the stent provides long- term support, precluding it from collapsing or narrowing again. The utmost ultramodern stents are medicine- eluting, meaning they sluggishly release drugs to help scar towels from forming andre-blocking the roadway.
In short
- Angioplasty Opens the roadway using a balloon.
- Stent Keeps the roadway open after it’s been widened.
Together, these procedures form a life- saving combination in cardiac care, especially during heart attack operation.
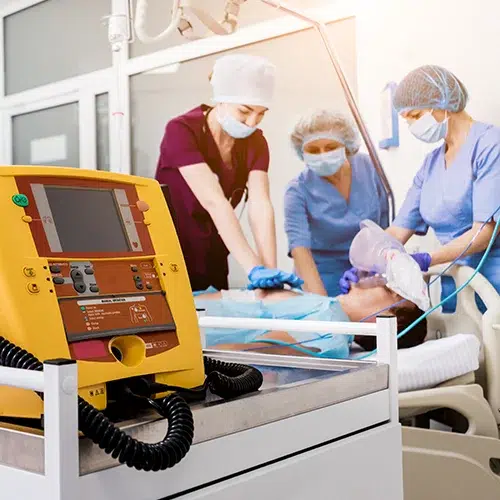
3. The part of Angioplasty and Stents in Urgent Care
In Urgent Care settings, medical brigades frequently serve as the first askers in relating cardiac extremities. Although advanced interventions like angioplasty or stent placement are generally performed in technical hospitals, critical care centers play a critical part in early opinion and stabilization.
Then’s how
- Performing an ECG( electrocardiogram) to describe abnormal heart measures.
- Monitoring vital signs and relating symptoms of casket pain or briefness of breath.
- Administering original oxygen, aspirin, or nitroglycerin before transferring the case to a sanitarium equipped for angioplasty.
By feting the warning signs beforehand and acting snappily, critical care professionals can significantly increase the case’s chance of survival.
4. When is Angioplasty Preferred Over a Stent?
While both angioplasty and stent placement are frequently used together, there are cases when angioplasty alone may be sufficient.
Angioplasty alone may be preferred when
- The roadway blockage is temporary or mild.
- The case has bleeding pitfalls or can not tolerate stent specifics.
- The blockage occurs in a small roadway where placing a stent is technically grueling .
Still, in utmost ultramodern cardiac procedures, stents are routinely used after angioplasty to reduce the threat of restenosis(re-narrowing of the roadway).
5. Recovery and pitfalls What to Anticipate
Both procedures are fairly safe but carry some pitfalls, as with any cardiac intervention. Common side goods may include mild bruising at the catheter point or short- term discomfort. Rare complications include bleeding, infection, orre-narrowing of the roadway.
Recovery highlights
- Cases generally stay in the sanitarium for 1 – 2 days after the procedure.
- utmost can return to normal conditioning within a week.
- Croakers frequently define blood- thinning specifics to help clots from forming around the stent.
Cases are encouraged to borrow heart-healthy cultures including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and quitting smoking — to maintain long- term heart health.
6. How Critical Care Contributes to Faster Cardiac Response
In cardiac extremities, time equals heart muscle. Critical Care centers serve as pivotal islands between symptom onset and technical treatment. Their part is n’t to perform angioplasty or stent procedures but to triage and stabilize cases before immediate transfer to an equipped installation.
Some crucial benefactions include
- Quick ECG interpretation for early heart attack discovery.
- Administering anti-clotting specifics like aspirin.
- Coordinating with emergency medical services( EMS) for rapid-fire sanitarium transfer.
- Educating cases on getting heart attack symptoms beforehand.
By syncopating the time between original symptoms and technical treatment, critical care centers help ameliorate issues in heart attack operation.
7. The Future of Cardiac Emergency Care
With advancements in technology, angioplasty and stent procedures have come safer, briskly, and more effective. Unborn inventions are concentrated on bioabsorbable stents, which dissolve naturally over time, leaving the roadway clear and flexible. Also, the integration of AI- powered cardiac diagnostics in critical care centers allows for quicker recognition of high- threat cases.
Combining these technological improvements with better critical care systems ensures that heart cases admit timely, life- saving interventions — no matter where they seek original treatment.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between Angioplasty vs Stent is n’t just for medical professionals it’s pivotal for anyone concerned about heart health. Both procedures play vital places in restoring blood inflow and precluding severe cardiac damage. In Urgent Care settings, early discovery and nippy action can make the difference between life and death.
As medical wisdom continues to evolve, the collaboration between critical care providers and technical cardiac brigades ensures better issues for cases worldwide. Feting symptoms beforehand, acting snappily, and getting the right treatment remain the keys to saving lives.