Commitment to administrative automation. However, a newer class of technology, known as agentic AI, is poised to take operations in healthcare to a fundamentally different level. Rather than merely making suggestions or augmenting tasks, such intelligent agents will be capable of autonomous planning, action, and adaptation within complex health care workflows. healthtechmagazine
In this article, we’ll explore what agentic AI means within the healthcare context, the operational challenges it helps resolve, the concrete solution patterns now emerging, and how healthcare organisations can prepare for the adoption of this next-generation capability. This isn’t about hype; it’s about how operations-not just care delivery-can be transformed.
What is Agentic AI and Why Does it Matter in Healthcare
To understand agentic AI, it’s useful first to contrast it with traditional AI or automation:
Traditional AI can identify patterns or provide recommendations, but agentic AI takes that to the next level-it performs workflows and then adapts the behavior based on the results.
According to IBM, “agentic” AI consists of “AI agents…created to handle specific tasks and processes” with a degree of autonomy.
Agentic systems in the case of healthcare can intervene in multi-step processes that might include anything from detecting a patient’s deteriorating vitals, initiating a triage protocol, notifying the care team, and triggering resource allocation, without manual orchestration
Why this matters: Healthcare operations are often complex, highly regulated, and involve several interacting systems: clinical, administrative, financial, regulatory, and supply chain. Agentic AI offers the prospect of introducing autonomy, adaptability, and real-time decision-making into those workflows, reducing human bottlenecks and improving reliability.
Key Operational Challenges in Healthcare That Agentic AI Can Address
There are many persistent issues in healthcare operations; agentic AI addresses several of them.
1. Fragmented workflows & systems
In most cases, different departments are isolated from each other, which can include clinical, financial, supply chain, and record information. These silos create delays in decision-making, duplicate efforts, and waste valuable resources.
2. Staff shortages and burnout
Clinicians and administrative staff are overburdened; routine and semi-routine tasks consume time that could be spent on high-value care.
3. Forecasting and Resource Allocation in Real Time
Hospitals need to plan bed capacity, ICU equipment, staffing levels, and inventory-often with incomplete data and a dependency on manual processes.
4. Complex Compliance and Risk Oversight
Healthcare operations need to be compliant with requirements for privacy, regulations, billing, and auditing, but also responsive.
5. Need for faster decision loops
From alerts about patient deterioration to supply chain disruptions, speed matters-but manual processes slow things down.
With agentic AI, the system can manage workflows autonomously, optimize resource moves, detect risks earlier, and act on insights without waiting for a manual trigger.
How Agentic AI is being applied across healthcare operations
Here are concrete solution patterns showing agentic AI in action.
Intelligent Scheduling & Capacity Planning
Some examples include the following: An AI agent monitors inbound patient data-ER arrivals, seasonal illness spikes, imaging backlogs-calculates predicted demand, and triggers the scheduling of staff, opening of additional nursing stations, or redeployment of equipment, all with little human intervention.
Automated Claims & Prior Authorization Processing
Instead of manual reviews of insurance claims or authorisations, an agentic system rapidly reviews patient records, eligibility, past authorisation history, predicts denials, flags issues, and can even initiate corrective workflows.
Patient Flow Orchestration
An agentic system tracks bed occupancy, diagnostic delays, patient preparation, and current status in real time from admission to discharge and intervenes, adjusting discharge times, optimizing transport, and dynamically scheduling labs to keep the flow smoother.
Supply Chain & Equipment Maintenance Automation
Agents can monitor the usage of high-cost devices such as MRI and ventilators, identify wear patterns, and schedule preventive maintenance or redeploy equipment based on forecasted need as a result; this cuts down on downtime and cost.
Virtual Care Coordination Agents
Agentic systems for remote monitoring and chronic disease continuously ingest data from devices or apps, detect risk thresholds (e.g., for patients with heart failure), escalate follow-ups, and coordinate care team interventions automatically.
Real-Time Clinical Decision Support
In the most complex situations, agentic modules interpret EHR data, imaging, genomics, and clinical guidelines, propose next-step treatment, and orchestrate care team activities, scheduling further diagnostics and creating alerts, all with learning from outcomes.
Why Agentic AI Offers a Step Change vs. Traditional Analytics
Several key differentiators make agentic AI more impactful for operations than earlier analytics or automation:
Adaptive learning: The system adapts according to context, outcomes, and emerging conditions, not fixed rules alone.
Multisystem orchestration: Agents coordinate across systems, teams, and workflows-not around a single task.
Continuous execution: Agents execute in real-time, monitor for changes, and act without waiting for a human to direct them.
Autonomy with oversight: While they are still ultimately overseen, they reduce the level of manual intervention required and free up staff for higher-value work.
Solution Building: How to Adopt Agentic AI in Healthcare Operations
Adopting this next-gen approach requires thoughtful planning. Herein is a roadmap on how healthcare organisations can commence implementing agentic AI.
Step 1: Define Operational Use-Cases
Start with clear operational pain‐points—e.g., “reduce ICU bed idle time,” “automate prior authorisations,” or “predict device downtime.” Focus on workflows that cross boundaries: clinical + admin.
Step 2: Data Strategy & Integration
Agentic systems will require high-quality, real-time data from EHRs, scheduling systems, device sensors, claims, and many others. Lay down data pipelines, governance, and interoperability frameworks.
Step 3: Select or Develop Agentic Architecture
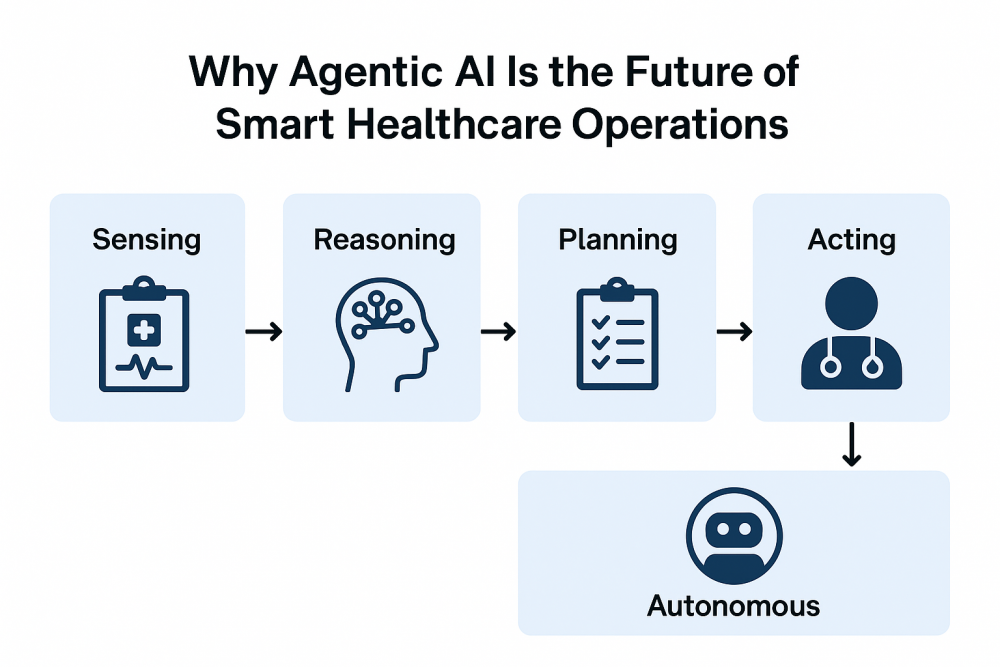
Implement a framework of AI agents that could include a perception module ingesting data, a reasoning/planning module selecting actions, and an execution module triggering workflows. Refer to the emerging frameworks for agentic systems.
Step 4: Governance, Ethics & Safety
Because agents will act with significant autonomy, ensure clear oversight, auditability, fail-safe rules, and compliance with healthcare regulations about privacy, device safety,and traceability.
Step 5: Pilot, Monitor, Learn
Start with narrow scope pilots, gather performance data, tune models, monitor for unintended behavior, and scale narrowly. Understand outcomes again, not just alerts created, but workflows completed, cost savings, and time-to-action.
Step 6: Scale and Embed into Operations
Embed successful agentic workflows into standard operations, integrating them with executive monitoring, and continually tune agents as business needs evolve.
Solutions Landscape: Tools & Services for Agentic AI Deployment
Building this type of system requires special capabilities; the selection of partners and services for agentic execution focuses on this. Organizations can outsource AI agent development services for autonomous workflow composition, data integration, and scalability. These services often provide pre-built agent frameworks and healthcare-specific orchestration mechanisms or integrate with existing systems.
Challenges and Considerations
While promising, agentic AI is not without risks or hurdles. Organizations should be aware that:
Data Quality & Availability: Agents only work well when there is consistent, reliable input data.
Integration complexity: Agentic systems frequently reach across several legacy systems and data silos.
Ethical and regulatory considerations: Decision-making automation in healthcare should be aligned with clinical responsibility, patient consent, and compliance.
Maturity and ROI: Industry observers caution that many agentic AI initiatives are still early-stage; business value may take time to materialise.
Why This Matters for Smart Healthcare Operations
For healthcare organisations committed to operational excellence and digital transformation, agentic AI offers a path to:
- Faster care transitions, fewer delays, smoother patient flow
- Reduced administrative burden on clinicians and support staff
- Smarter resource allocation and lower operational cost
- Better response to unpredictable events (surge demands, device failures)
- Elevated patient experience through more timely and coordinated care
In effect, agentic AI positions operations to move from reactive to proactive, from managing crises to orchestrating care.
Conclusion
Agentic AI is emerging as a powerful enabler for smart healthcare operations, bringing autonomy, orchestration, and continuous learning into workflows that previously required heavy manual coordination. While adoption is still nascent, the core capabilities of autonomous agents planning, acting, and adapting fit the needs of modern healthcare organisations facing complexity, scale, and demand for efficiency.
For organisations looking to take the next step in operational transformation, aligning with specialised AI agent development services can help build the infrastructure, governance, and integration necessary to deploy this next generation of intelligent operations.
The future of healthcare operations is not just about smarter analytics; it’s about autonomous workflows, seamless orchestration, and operational intelligence powered by agentic systems that support clinicians, administrators, and patients alike.